⬤ General Motors has executed one of the most aggressive buyback programs among major U.S. automakers in recent years. The company has repurchased roughly 38% of its outstanding shares over the past four years. Total shares outstanding dropped from approximately 1.45 billion in late 2021 to about 904 million by the end of 2025.
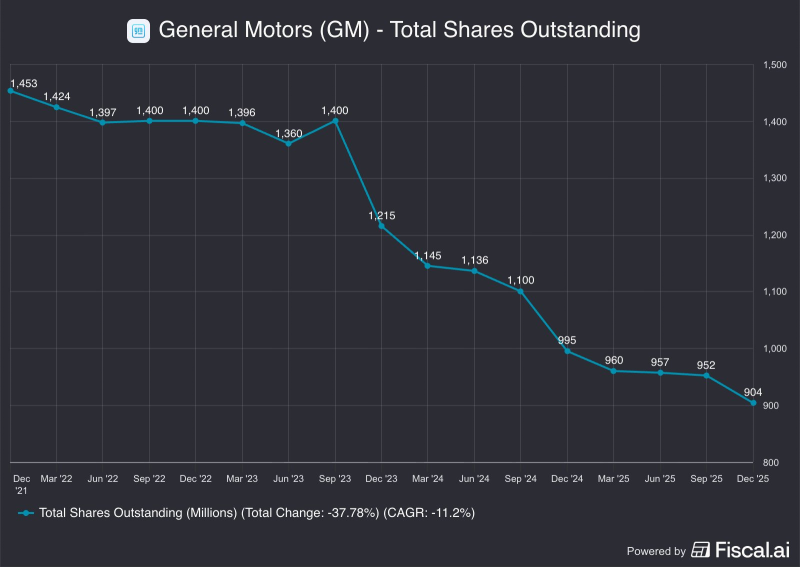
⬤ The reduction reflects sustained, methodical execution rather than one-off events. GM's share count stayed relatively stable through most of 2022 before buybacks accelerated from mid-2023 forward. The steepest drop came between late 2023 and late 2024, when shares outstanding plunged from around 1.4 billion to near 1.0 billion. The full-period decline of 37.78% represents an annualized reduction rate of approximately 11%.
⬤ GM maintained its capital return focus throughout, retiring nearly 550 million shares over four years despite ongoing investments in EVs and autonomous tech. Buybacks became central to GM's capital allocation strategy, steadily reducing dilution and fundamentally reshaping the company's equity structure.
⬤ Large-scale share reductions can materially impact per-share metrics and valuation comparisons within the automotive sector. Sustained buybacks amplify earnings per share trends and reshape how markets view capital structure—especially critical in capital-intensive industries. GM's ongoing share reduction highlights how capital allocation choices shape market narratives around corporate discipline and financial strategy, while raising questions about balancing shareholder returns against long-term investment needs.
 Marina Lyubimova
Marina Lyubimova

 Marina Lyubimova
Marina Lyubimova


