A commodity is an ancient form of financial instrument. The commodity market is almost the same age as human civilization itself. Historical evidence suggests that rice was probably the first commodity about 6,000 years ago. In the days of Sumerian civilization (4,500 BC), people used clay tokens as a form of money to buy livestock.
Today, commodity trading forms the backbone of the global trading ecosystem. With the advent of online commodity trading, private traders have gained access to global commodity markets with a relatively modest amount of capital.
Commodities have become a popular means of hedging inflation and portfolio diversification. For many traders and investors, commodity trading is the preferred way to protect funds and reduce the overall risk to their portfolios.
What is a tradable commodity?
Tradable commodities are basic goods that are used in the commerce world. Mostly, these are interchangeable with similar goods, which fall in the same category.
There are four major types of tradable commodities.
- Energy
- Metals
- Agriculture
- Livestock
A commodity is considered tradableif it can be traded easily. Moreover, any commodity that can be accessed from major exchanges is called a tradable commodity.
For instance, wheat, cattle, trade corn, and others are ‘tradable commodities’.
Furthermore, these are those commodities that can be traded via futures contracts. You can exchange them on different exchanges including ICE or CME for that matter.

Tradable commodities are storable and they can be perished.
For example, gold, energy, silver, copper, cattle and such, are those that are considered ‘tradable’ commodities.
Moreover, tradable commodities are exchanged for another commodity off and in the same category.
For instance, gold can be changed and exchanged for gold and cattle can be exchanged for cattle.
Additionally, you can trade tradable commodities in different exchanges. For example, the London Metal Exchange, the Chicago Board of Trade, Intercontinental Exchange and others.
On the other hand, there are many ways through which you can invest in tradable commodities. The most common is futures.
Futures
One way to invest in commodities is through a futures contract.
Moreover, future contracts are agreements to buy/sell a specific quantity of a commodity at a designated price and at a later point in time.
Furthermore, futures are available on each category of a given commodity.
Whereas, there are different tradable commodities available, the most tradable ones are:
- Platinum (PL)
- Gold (XAU)
- Oil (CL)
- Soybeans (ZS)
- Heating Oil (HO)
- Sugar (SB)
- Wheat (ZW)
- Copper (HG)
Tradable commodities are ‘interchangeable goods’.

Additionally, while tradable commodities are interchangeable, some other commodities are not. These are called non-tradable commodities.
Tradable commodities are executed through future contracts. These are executed on exchanges that standardise the minimum quality and quantity of products traded.
If we go into deeper details of what tradable commodities are, or what are tradable commodities, we establish that:
- Tradable commodities are exchangeable via different exchanges
- These are long term things and tradable commodities are perishable. They can be purchased at a given time and then sold at a specific price later on through future contracts
- Moreover, one tradable commodity will be exchanged for another tradable commodity of the same type

How to make money on commodities?
Commodity trade has been growing rapidly since clay tokens for livestock exchange appeared. In the past, there were various commodities that institutions and investors used to trade. For example, commodity bonds allow traders to trade on price fluctuations, without having to store and deliver the product.
In fact, a trader trades in contracts for the future delivery of goods. A trader pays a contract at a fixed price. If the price rises from the moment the contract is acquired, then upon expiration of the contract the trader will make a profit. If the price drops, the trader loses money.
However, even this type of trade can become extremely complex. Futures markets often have different delivery times and transaction volumes. This is one of the reasons why many traders trade CFDs on commodities.
Peculiarities of commodity trading
The market of commodities has its own downsides when it comes to trading. Speculation plays a major role in the formation of this sphere. Here are the peculiarities:
- The market is less dynamic, and specialists highlight slow overall development of this market in comparison with the market of finished goods;
- Usually a very high concentration of the supply of the majority of raw materials in a limited number of countries;
- Often unstable and in many cases extremely contradictory market conditions;
- Price volatility, and often their sharp fluctuations;
- The market is highly dependent on natural and geographical factors, and the raw materials market of plant origin on climatic and weather conditions;
- The significant role of long-term contracts in international trade in many types of mineral raw materials and fuels.
Global markets for raw materials and investment projects in the field of environmental management are rigidly divided. The global fuel and raw materials market is currently characterized by fierce competition. Free niches in this world market are extremely rare, since the largest world producers from industrial countries, capable of influencing the trade policy of their countries, are not interested in the appearance of new sellers offering raw materials at low prices.
The most attractive countries for investing in the development, production, and processing of minerals are those countries in which a stable economy and political situation are observed. Such investment is quite long-term, and therefore even large multinational corporations try to minimize their risks.
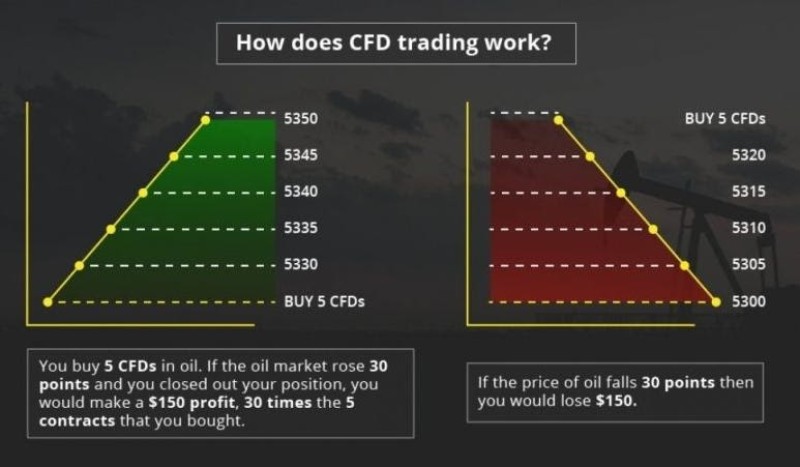
Commodity CFD Trading
CFD (or contract for difference) allows the trader to speculate on the rise and fall of the market, without owning the product. CFDs were created in the early 1990s in London by two investment bankers, UBS Warburg.
In fact, CFD is a contract between two parties - a trader and a broker. At the end of the contract, participants receive the difference between the opening and closing a position in cash.
Simply put, a trader pays the difference between the opening and closing prices of the goods he is trading in. The ease of opening and closing positions compared to other markets is just one of many reasons why CFDs are so popular.
This does not mean that trading CFDs on commodities is an easy process, but it definitely has more advantages over other markets.
Advantages of trading CFDs on commodities:
- Leverage level. A retail trader can trade assets exceeding the investment balance by twenty times. A professional trader can trade assets five hundred times the balance.
- Trading is available 24/5. Traders can trade twenty-four hours a day, five days a week, gaining access to various goods and markets from around the world.
- Zero commission. Traders can trade with zero commissions – orders start from €200.
- Profit from a rising and falling market. If you correctly understood the direction of the market and the movement of prices! Otherwise, there may be a loss.
Pros and cons of commodity trading
Advantages of commodity trading:
- Diversification. An analysis of the data shows that there is a low or negative correlation between commodity prices, stock exchange rates, and bond rates. This allows hedging in relation to equity investments.
- Inflation protection. While inflation weakens bond and stock prices, it has a positive effect on commodity prices. This is quite logical: as a result of inflation, prices for products, as well as for the raw materials from which these products are made, are rising.
- Development opportunities. As the demand for certain commodities increases, the price of them rises accordingly. For example, over the past two years, the cost of palladium futures has more than doubled, as this material is used universally for the manufacture of certain automobile parts.
Disadvantages of commodity trading:
- High volatility. It is believed that commodity trading is characterized by maximum volatility: on average, this indicator is twice as high as stock volatility and four times as volatile as bonds.
- High primary order prices. The minimum recommended deposit for trading is around $250-300.
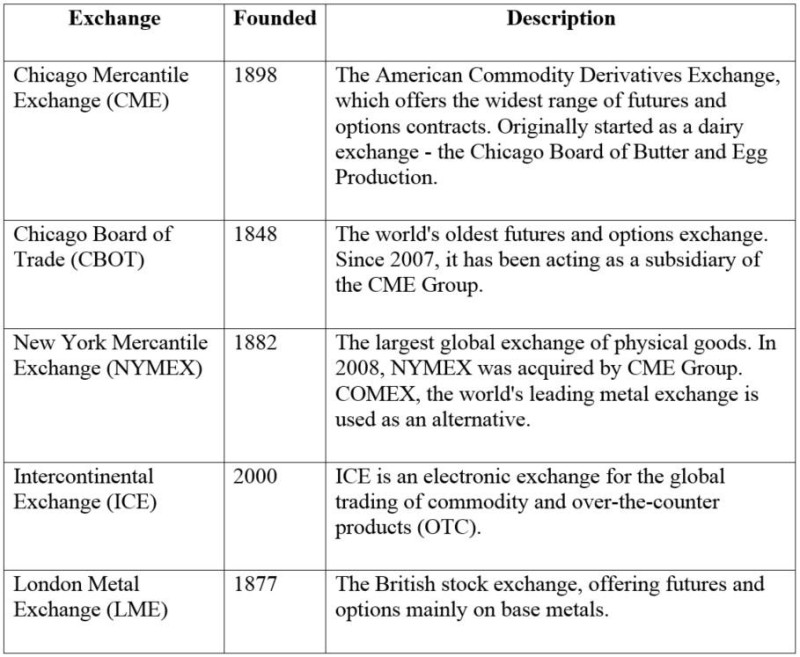
Where to trade commodities?
Here are the biggest and most well-established exchanges:
Summary/Conclusion
Moreover, if we talk about tradable commodities, there are different kinds of these.
There are soft commodities, hard commodities, energies commodities, financials commodities, grains, and others.
- Soft tradable commodities include cotton, orange juice, cocoa, livestock, and others. It plays a crucial role in the future market.
- Hard commodities include gold, silver, and others. These usually play an integral role in a country and improve a country’s economic health.
Other known tradable commodities include energies (petroleum, byproducts of petroleum, natural gas, crude oil etc.).
Grains are also tradable commodities. They include rice, soybean, oats, wheat, and others.
Tradable commodities, therefore, are those that are easily exchangeable through futures contracts or other means. Learn more about them by staying tuned at The Tradable.
 Peter Smith
Peter Smith

 Peter Smith
Peter Smith


